
Mulching in agriculture refers to the practice of protecting the soil with organic or synthetic substances to conserve moisture. It even helps suppress weed growth, moderate soil temperature, and enhance soil fitness. We will discuss the numerous advantages of mulching, along with more desirable crop yields, decreased water utilization, and weed manipulation, at the same time as knowing the method of mulching and its role in sustainable farming practices.
What is Mulching?
Mulching is a process of covering the soil to retain soil moisture and control the development of weeds. Also, it acts as a contributor to soil fertility. Mulching in agriculture can either be done organically or inorganically, permanent or temporary, based on the requirements of the farmers. Compost, dry leaves, hay, and straw are some of the organic mulch materials. There are different types of plastic mulching sheets also available in the agricultural industry for use as inorganic Mulching. To know more about Mulching, its types, techniques and benefits, keep reading.
Where can you do Mulching?
Mulching farming can be done in various places, including farms, gardens and landscapes in order to preserve soil moisture, control weeds, regulate temperature and improve soil health. Apart from gardens, landscapes and farms, Mulching uses in orchards, vegetable rows, raised beds, pathways, around trees, in containers, nurseries and greenhouses, depending on your specific goals and requirements.
When should you do Mulch?
You should do Mulching farming at various events depending on your specific requirements. You should do Mulching during:
Early Summer: It will help maintain consistent moisture and temperature during hot and dry spells.
Late Fall or Winter: Mulching during this time period protects plant roots from freezing by insulating the soil.
Spring: Applying Mulch during this season will support retaining moisture and controlling early weeds with the rise in temperature.
Around New Plantation: Mulching plants help to establish and strengthen them.
After Rain or Irrigation: Mulching in agriculture helps lock the moisture.
When Weed Growth is a Concern: Apply Mulch during this period as much as needed to suppress weeds.
Throughout the Growing Season: Soil Mulching should be done in vegetable gardens throughout the growing season in order to control weeds and maintain good soil moisture.
Types of Mulching

Considering the mulch materials used in the process, there are two types of mulching in agriculture: organic and inorganic. In organic Mulching, mulches are prepared using plant sources, including compost, grass clippings and more. Inorganic Mulching incorporates mulches derived from plastic or other equivalent resources.
Also Read – What is Organic Farming in India
Organic Mulching
This type of mulching is performed using organic mulch materials called organic Mulching. Here, we have listed mulch materials that are frequently used for organic Mulching process.
Grass Clippings
Grass clippings or grass from mowed lawns are among the most preferred organic mulch materials among farmers for mulching of soil. A thin layer of the grass clippings is spread over emerging seedlings, and later on, a thick layer of dry grass is applied in the crop area. Moreover, farmers should avoid using grass clippings treated with pesticides as Mulch. The decomposition of grass clippings supplies nitrogen to the soil.
Straw and hay
These are the other most commonly used organic Mulching materials in agriculture. This is because straw and hay have a long life as compared to other materials used as Mulch. Also, they help to make the soil more fertile upon its decomposition. Straw and hay help maintain a cool enviornment by reflecting light from the surface of the soil. There are chances that the crop can get weeds, but the application of a thick layer of straw can prevent it. In addition, it is good to apply nitrogen fertiliser to the soil before straw mulching because straw is high in carbon and consumes nitrogen from the soil.
Leaves
The fallen leaves from deciduous trees collectively form the best material for mulching of soil. Since they are great insulators and helpful for root crops like carrots and parsnips.
Peat Moss
This is a mulch material that long-last in nature and is known for lowering the pH of the soil. So, it is used in the crops that demand acidic soil conditions.
Inorganic Mulching
Farmers prefer to use inorganic Mulching process incorporating inorganic mulch materials (plastic mulching) when they do not get organic Mulch. These mulching sheets are available in different colors and sizes as per the requirements. The inorganic mulch types are as follows.
Transparent Mulch
The transparent mulch sheet allows passing light and helps in weed growth. However, the use of herbicide on the inner surface of the film keeps the weed growth in check. This type of mulching sheet is used for soil solarisation in nurseries in order to attain 100% seed germination and a disease-free nursery. Also, it plays a vital role in hilly areas in order to increase the temperature of the soil during the winter season.
Black Mulch
The black Mulch, on the other hand, prevents sunlight penetration to the soil. Consequently, the photosynthesis process stopped below the black film. This type of mulching in agriculture aids in controlling the weed growth and increasing the soil temperature.
Double Coloured Mulch
These types of mulching paper are basically wavelength selective and prevent certain wavelengths from the sun’s radiation from passing by. This way, the sunlight changes and affects the growth and development of the plants. It is considered that these films control the different characteristics of a plant, including the fruit colour, size, root development, height and much more. In addition, these coloured mulching sheets re-emit less heat, which helps maintain the lower leaf temperature. Some of the most popular double-coloured mulch varieties are Red-black, White-black, Silver-black and Yellow-black/brown. They have their own properties and support different requirements of the farmers as per the crop.
Degradable Mulch
There are two types of degradable mulching paper available in the market- photo-degradable and bio-degradable Mulch. As the name suggests, the photo-degradable Mulch disintegrates under the sun over a certain period of time. Similarly, the bio-degradable Mulch also disintegrates under natural environmental conditions after a certain period of time.
How to Choose Mulch Material?
The selection of the right mulch is highly important as mulches have certain properties that are necessary to deliver the maximum mulching benefits. With organic Mulch, its characteristics can not be altered, but inorganic or artificial Mulch should be selected according to their specific attributes and your farming requirements. The important aspects one must consider while choosing the mulch material are:
Thickness
The thickness of the material has little or no impact on Mulching except for the solarisation of the soil. However, the thickness of an artificial mulch film should be between 15-30 microns for vegetable crop mulching. For orchids, it should be 100-150 microns and for small-duration crops, the mulch film thickness should be 25 microns.
Width
The width, on the other hand, should match the inter-row spacing. Under general growing conditions, the average width of the film should be around 1 or 1.5m.
Colour
The colour of the Mulch affects soil temperature, the air temperatures around the plants, weed growth, the incidence of insects and the salinity of the soil.
Perforation
If you want to distribute water and fertilisers to the crop efficiently, you should select unperforated Mulch. But, if you want to prevent water stagnation around the plants, you should go with the perforated film. However, it may encourage weed growth.
So these are the things one should consider before choosing the mulch material.
Mulching Techniques
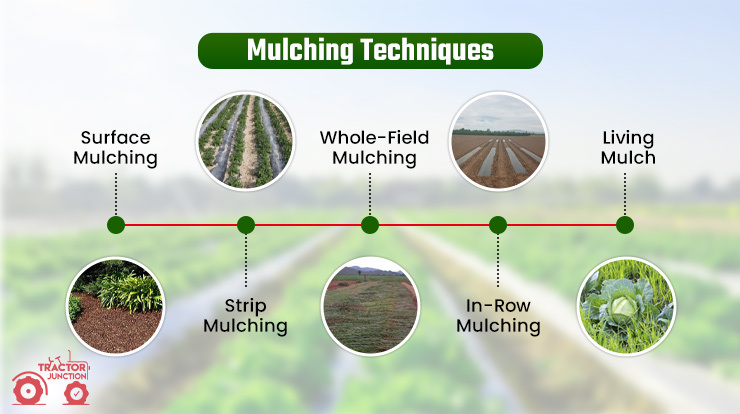
Mulching is a versatile agricultural practice that offers various advantages to crops and soil. Here are some common mulching techniques utilized by farmers:
Also Read – Types of Farming in India
Surface Mulching
- Surface mulching includes spreading a layer of mulch material straightforwardly on the soil surface around plants.
- This procedure assists with conserving soil dampness by diminishing evaporation, suppressing weeds by obstructing daylight, and controlling soil temperature.
- Organic materials like straw, hay, or grass clippings are normally utilized for surface mulching. However, plastic or fabric mulches can likewise be applied.
Strip Mulching
- This mulching technique includes applying Mulch in narrow strips or rows between crop rows, allowing the space between rows to be uncovered.
- This method considers better water penetration and air movement in the soil while providing weed suppression and dampness maintenance in the mulched strips.
- Plastic Mulching or landscape fabric is frequently utilized for strip mulching, as it tends to be laid in precise rows utilizing specific gear.
Whole-Field Mulching
- Whole-field Mulching covers the whole field with a layer of mulch material, giving uniform protection and advantages to the whole soil surface.
- This mulching method is regularly utilized in orchards, vineyards, and perennial crop systems where weed control, dampness maintenance, and soil health are crucial.
- Organic mulch materials, for example, straw or compost, can be spread evenly across the field utilizing apparatus, while plastic mulching can be laid utilizing plastic mulch layers.
In-Row Mulching
- In-row mulching includes setting Mulch straight around individual plants or rows of crops, leaving the space between rows uncovered.
- This mulching technique is valuable for protecting young plants from weeds, retaining soil moisture, and reducing soil erosion around the root zone.
- Organic mulch materials like wood chips, destroyed bark, or compost can be applied as in-row Mulch, giving a protective layer while considering air and water exchange.
Living Mulch
- Living Mulch includes establishing low-growing cover crops or enduring ground covers between rows of main crops to give persistent soil mulching and advantages.
- Cover crops like clover, vetch, or rye can assist with suppressing weeds, improving soil structure, and enhancing supplement cycling while serving as a living mulch.
- This mulching method also supports valuable bugs and pollinators, adding to overall ecosystem health and strength.
By using these mulching techniques, farmers can effectively improve soil health, save water, suppress weeds, and improve crop productivity in a maintainable and environmentally friendly manner. Picking the right mulching approach relies upon elements such as crop type, environment, soil conditions, and cultivating objectives.
How to Do Mulching?
Mulching farming is done differently for both the larger and smaller plants. For the larger plants, the mulch materials are spread around the plant and between the rows. For smaller plants, the way of spreading mulch materials remains the same but is not too close to the base in order to avoid disease incidence.
Irrigation System
When it comes to the irrigation of mulched land, drip irrigation is considered the most suitable way of watering the crop. The laterals are placed under the Mulch. For intercropped areas, the laterals can be placed above the Mulch to adjust the emitters.
How to Dispose Mulch Sheets?
Mulch material should be disposed of properly so that the soil doesn’t get contaminated. The organic and degradable inorganic Mulch gets degraded in the soil. But the mulch materials like plastic are not degraded by the soil. Therefore, it is necessary to dispose of such mulching sheets properly.
Advantages of Mulching in Farming

Mulching in farming offers a number of advantages for the cultivators, apart from weed control and water conservation. Here, we have mentioned the mulching benefits, which are as follows.
- Helping weed control by limiting the energy supply to the weeds, is one of the advantages of mulching.
- It helps conserve water by preventing direct evaporation of water from the soil. That’s why you don’t need much water for irrigation.
- In addition, it helps retain moisture in the soil for a longer period of time and controls humidity levels within the plant root zone.
- With mulching farming, you can develop the white root of the plant above the surface of the soil.
- You can keep insects away from the plants because the mulching sheets reflect light that limits the incidence of pests to a great extent.
- Mulching soil conservation protect the soil from erosion during heavy rainfall because it has no direct contact with the rain.
- It reduces the salinity level of the soil and prevents leaching of fertilisers as well.
- Moreover, it encourages seed germination, early maturity, and higher production.
Disadvantages of Mulching in Agriculture

Apart from the various advantages of Mulching, there are several disadvantages of mulching as well. Here, we have listed some to make you aware of them as farmers.
- If you deep Mulch when the soil is already wet, it will create excess moisture in the root zone. This will result in stress on the plant and rotten roots.
- Mulch piled up against the trunk or stem, can cause stress on the stem tissues and encourage the development of pests on the tree trunk or lead to stem girdling roots.
- Also, if Mulch is piled high against the stems of the young trees, then this may attract rodents that can chew the bark and girdle the trees.
- The mulch material containing fresh grass clippings, can cause nutrient deficiencies in the soil by altering the pH level of the soil. Also, it can develop toxic levels as well.
- When you use fine Mulch as thick as a blanket, it mats and reduces the penetration of water and air.
- If you use ‘sour’ Mulch, which remains anaerobic in nature and has a pungent smell, this Mulch may contain alcohols and organic acids that can prove toxic to the young plants.
Conclusion
This is all about Mulching in agriculture. If you are a farmer and grow crops, Mulching is mandatory. This blog will prove to be highly beneficial for you since it covers each and every thing associated with Mulching. From mulching types and techniques to the right way of doing Mulching, its benefits, drawbacks and much more. By having such a great knowledge about Mulching farming, you can grow a healthy crop that will generate a good income for you.
For more such farming-related blogs, keep visiting the Tractor Junction.
FAQs:
Q1. Is mulching a soil management method?
Ans. Yes, mulching is a soil control technique that involves covering the soil with a layer of natural materials for diverse advantages.
Q2. How is mulching a method of soil conservation?
Ans. Mulching prevents soil erosion by way of protecting the ground with a protective layer, lowering water runoff, retaining moisture, and improving soil fertility.
Q3. What is surface mulching?
Ans. Surface mulching involves covering the soil with a layer of organic or inorganic fabric to conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and alter soil temperature.
Q4. What are the benefits of mulching?
Ans. Mulching conserves soil moisture, suppresses weeds, moderates soil temperature, and improves soil fertility, improving plant growth and productivity in the long run.
Q5. What are the objectives of mulching?
Ans. The objectives of mulching are conserving soil moisture, less the weed growth, moderating soil temperature, and improving soil fertility with its structure.
Related Blog
What is Apiculture?
What is Precision Farming?


